Toxic Multinodular Goiter Treatment
Toxic multinodular goiter treatment. Hypothyroidism 10 in 5 years. Through thyroidectomy your doctor will remove all or part of the thyroid gland to remove toxic goiter permanently. This procedure is performed when the size of the goiter becomes very large.
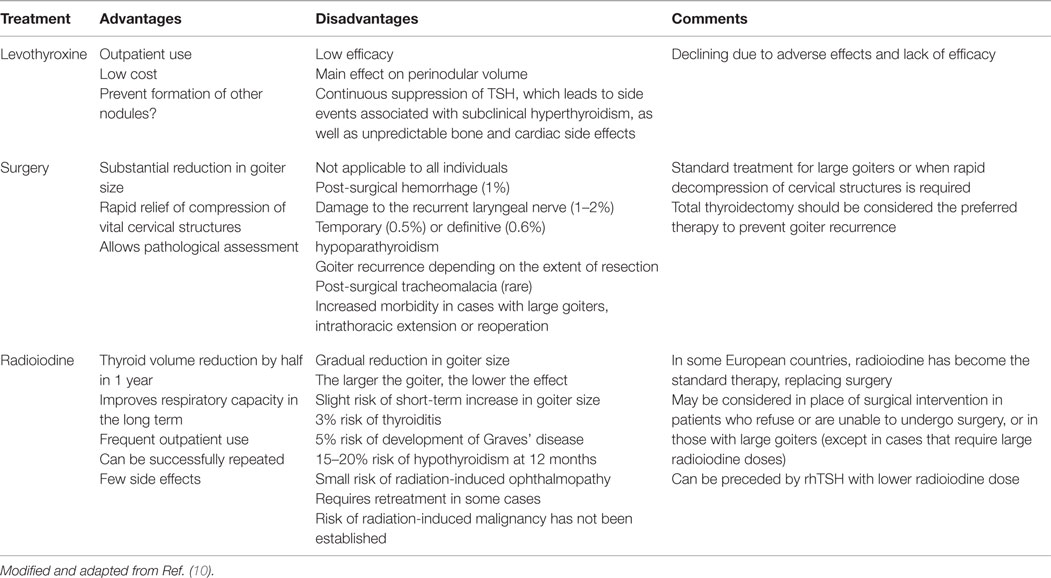
Therefore patients who have autonomously functioning nodules should be treated definitely with radioactive iodine or surgery. É uma das causas mais comum de hipertireoidismo a par da Doença de Graves. Although several other treatment modalities are currently available for the management of patients with multinodular goiters one must carefully weigh the riskbenefit of each option because some of these treatments such as levothyroxine suppressive therapy offer benefits that are less clear and may pose undue risk for certain patient populations.
One big concern with having a multinodular goiter is the risk of thyroid cancer. However the risk of hypothyroidism is 3 after 1 year and 64 after 24 years depending on the treatment modality and degree of TSH suppression at the time of radioiodine administration particularly for patients less than 50 years old. Not commonly used Slow reduction in the goiter volume.
In most of the cases doctors can cure and control toxic goiter. The medication helps reduce the size of thyroid tissue. N Engl J Med 2011.
Definitive treatment most commonly radioactive iodine is usually required. Radioiodine therapy for hyperthyroidism. About a quarter of the patients became.
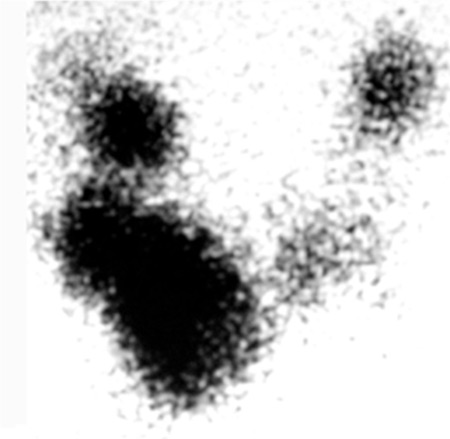
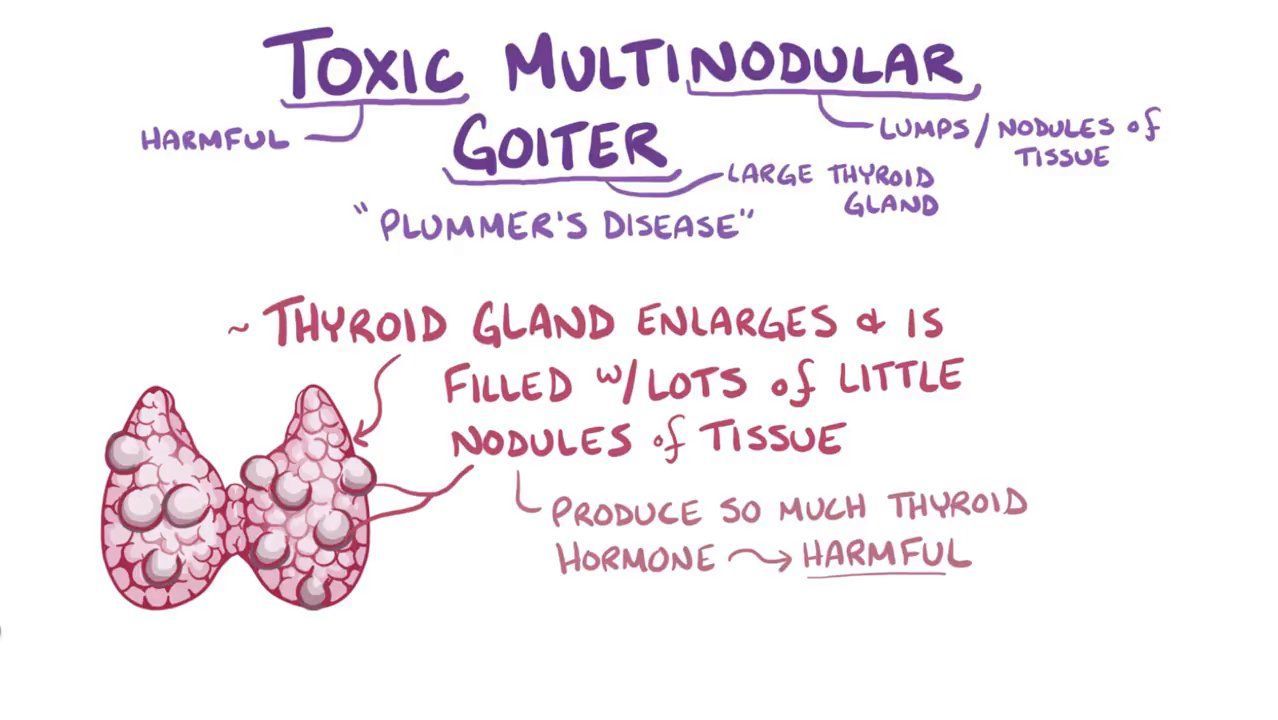
Radioactive iodine can be used to cure the hyperthyroidism from a toxic nodule or toxic multinodular goiter. Evidence-based management of toxic multinodular goiter Plummers Disease Treatment of Plummers disease with antithyroid medications ethanol ablation RI ablation or surgery must balance the goals of therapy durability of cure relief of symptoms risk of malignancy and risk of complications. If untreated complications may include sequelae of hyperthyroidism such as cardiac dysfunction or bone loss or tracheal compression by large goiters.
The need for additional radioiodine therapy is approximately 20 in patients with toxic multinodular goiter. 40 reduction in goiter volume in 2 years.
40 reduction in goiter volume in 2 years.
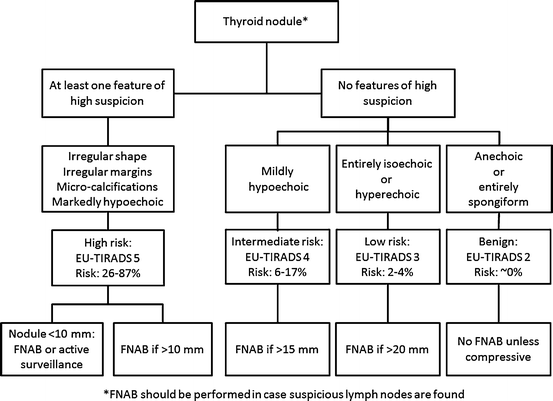
Radioiodine therapy for hyperthyroidism. One big concern with having a multinodular goiter is the risk of thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 2011. The need for additional radioiodine therapy is approximately 20 in patients with toxic multinodular goiter. For toxic multinodular goiter the size of the thyroid is important. The treatment of toxic multinodular with a fixed dose of radioactive iodine 15 mCi was effective in resolving hyperthyroidism in almost 90 of patients and significantly reducing the size of the goiter by more than half. This procedure is performed when the size of the goiter becomes very large. In addition to imaging techniques which are usually performed first TSH should be systematically assayed in goiter except in cases of solitary cold nodules. However the risk of hypothyroidism is 3 after 1 year and 64 after 24 years depending on the treatment modality and degree of TSH suppression at the time of radioiodine administration particularly for patients less than 50 years old.
Not commonly used Slow reduction in the goiter volume. Not commonly used Slow reduction in the goiter volume. Through thyroidectomy your doctor will remove all or part of the thyroid gland to remove toxic goiter permanently. Radioactive iodine can be used to cure the hyperthyroidism from a toxic nodule or toxic multinodular goiter. Therefore patients who have autonomously functioning nodules should be treated definitely with radioactive iodine or surgery. In addition to imaging techniques which are usually performed first TSH should be systematically assayed in goiter except in cases of solitary cold nodules. Porterfield JR Jr Thompson GB Farley DR et al.

































Post a Comment for "Toxic Multinodular Goiter Treatment"